Alarm fatigue generally results in a diminished response to alarms. Acceptable and well timed response to intravenous pump alarms is essential to infusion continuity.
The problem of filtering out vital quick half-life infusion alarms from nonurgent alarms is a key problem for danger administration for clinicians.
Crucial care areas present ample alternatives for intravenous treatment error with the frequent administration of high-alert, vital quick half-life infusions that require rigorous upkeep for continuity of supply.
Most critical treatment errors in vital care happen in the course of the execution of therapy, with performance-level failures outweighing rule-based or knowledge-based errors.One goal of this research was to ascertain baseline knowledge for the categories and frequency of alarms that vital care clinicians are uncovered to from quite a lot of infusion units, together with each giant quantity pumps and syringe drivers.
One other goal was to establish the quantity of those alarms that particularly relate to vital quick half-life infusions and to judge consumer response occasions to alarms from infusion units delivering these explicit infusions.The occasion logs of 1183 infusion pumps utilized in vital care environments and generally care areas throughout the European area had been mined for a variety of alarm states.
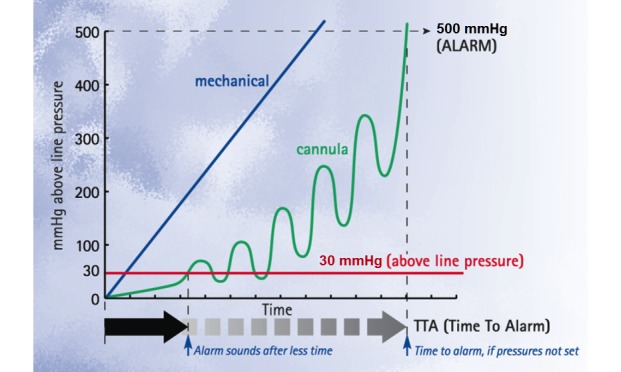
The research then centered on a choice of infusion alarms from units delivering vital quick half-life infusions that will warrant speedy consideration from clinicians in an effort to keep away from probably dangerous extended infusion interruption.
The response time of clinicians to infusion-interruption states and alarms for the chosen vital quick half-life infusions was then calculated.
Preliminary evaluation confirmed a imply common of 4.50 alarms per infusion within the basic vital care pump inhabitants versus the entire hospital fee of 1.39. Within the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) group, the alarms per infusion worth was considerably above the imply common for all vital care areas, with 8.61 alarms per infusion. Infusion-interruption of vital quick half-life infusions was discovered to be a major drawback in all areas of the final vital care pump inhabitants, with a major variety of downstream (ie, vein and entry) occlusion occasions famous.
Whereas the imply and median response occasions to vital quick half-life infusion interruptions had been typically throughout the half-lives of the chosen medicines, there was a excessive prevalence of outliers by way of response occasions for all of the vital quick half-life infusions studied.
This research offers a sign of what may be anticipated in vital care environments by way of the quantity of basic infusion alarms and significant quick half-life infusion alarms, in addition to for clinician response occasions to vital quick half-life infusion-interruption occasions.
This research additionally identifies probably problematic areas of the hospital for alarm fatigue and for explicit problems with infusion and infusion-line administration.
Utility of the proposed protocols will help create benchmarks for pump alarm administration and clinician response occasions. These protocols might be utilized to research on the affect of alarm fatigue and for the analysis of protocols, infusion-monitoring methods, and infusion pump-based treatment security software program aimed toward decreasing alarm fatigue and guaranteeing the upkeep of vital quick half-life infusions. Given the frequency of infusion alarms seen on this research, the chance of alarm fatigue because of the white noise of pump alarms current in vital care, to which clinicians are continuously uncovered, may be very excessive.
Moreover, the added difficulties of sustaining vital quick half-life infusions, and different infusions in specialist areas, are made clear by the excessive ratio of downstream occlusion to infusion begins within the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
The power to quantitatively observe the quantity of alarms and clinician response occasions contributes to a better understanding of the problems of alarm fatigue in intensive care models. This may be utilized to medical audit, can permit for focused coaching to cut back nuisance alarms, and might assist in planning for enchancment in the important thing space of upkeep of steady-state plasma ranges of vital quick half-life infusions. One clear conclusion is that the treatment administration rights needs to be prolonged to incorporate proper upkeep and ensured supply continuity of vital quick half-life infusions.